
It is important to understand the energy performance ratings of your windows and doors as it relates to their potential for gaining and losing heat. The National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC) provides information enabling homeowners to accurately compare window performance. Here is a summary of what gets measured and why.
U-Factor
U-Factor measures how well a window is insulated and prevents heat from escaping. While the U-Factor can take any value, typically windows range from 0.20 to 1.20. The lower the U-Factor, the better the window insulates. The lower the U-factor, the greater the window’s resistance to heat flow and the better its insulating value. U-value measures the rate of heat transfer through glass (glazing). U-values, depending on climatic conditions.
Solar Heat Gain Coefficient
Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) measures how well a window blocks heat from sunlight. It can range in value from 0 to 1. The lower the Solar Heat Gain Coefficient, the lower the level of visible light that can affect the brightness of a room’s interior, and the less solar heat the window lets in. The sun can provide free heat in the winter, but lead to overheating in warmer conditions. Selecting different types of Low E glass coatings allows for balancing Solar Heat Gain appropriately for each individual home. Certain products use spectrally selective glass that blocks infrared light while still allowing high levels of visible light—so you can daylight your home while maintaining comfortable temperatures.
To further understand SHGC, it’s important to note that it represents the amount of solar heat that passes through a window. This heat can be directly transmitted or absorbed and gradually released inside your home. A lower SHGC means less passive heat gain and greater shading ability, which is crucial for maintaining cooler indoor temperatures during hot months. Conversely, a higher SHGC indicates a higher capability for gathering solar heat, which can be beneficial during colder periods.
Like the U-factor, the SHGC appears on the labels of windows from reputable manufacturers, helping consumers make informed decisions. Understanding the SHGC values allows you to choose windows that best suit your climatic needs and energy efficiency goals.
Understanding the U-factor and SHGC for Window Selection
When selecting windows, the duo of U-factor and Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) plays a pivotal role in energy efficiency. Think of these two elements as the perfect blend of peanut butter and chocolate—each enhances the other to optimize your home’s energy performance.
What is the U-factor?
The U-factor measures how well a window prevents heat from escaping. A lower U-factor indicates better insulation, which is crucial for keeping your home warm during colder months.
Decoding SHGC
SHGC quantifies the window’s ability to block heat from sunlight. A lower SHGC is favored in warmer climates to minimize solar heat gain, while a higher SHGC can be beneficial in cooler areas to take advantage of warmth from the sun.
How Do They Work Together?
To choose the best windows, it’s essential to consider both the U-factor and SHGC based on your climate zone:
- Northern Climates:
- Opt for windows with a U-factor of 0.30 or below to maximize heat retention.
- Any SHGC value can be acceptable, but a higher SHGC (like 0.40) can be advantageous to harness solar warmth.
- North-Central Regions:
- Aim for a U-factor of 0.32 or lower.
- Pair it with an SHGC of 0.40 or less to balance insulation and solar gain.
- South-Central Zones:
- Prioritize a U-factor under 0.35 to ensure moderate heat retention.
- Choose an SHGC no greater than 0.30 to prevent excessive solar heat.
- Southern Areas:
- Look for a U-factor of 0.60 or less.
- An SHGC of 0.27 or lower helps keep interiors cool when temperatures rise.
By aligning the U-factor and SHGC with your specific climate needs, you’ll ensure that your windows not only improve energy efficiency but also enhance comfort throughout the year. Understanding these metrics is key to making an informed decision that saves on energy bills and reduces your environmental footprint.
VLR
Visible Light External Reflectance or VLR refers to the percentage of visible light that is reflected externally by the glass as detected by the human eye. The higher the VLR, the lighter your windows allow in your home.
Air Leakage
Air leakage is a natural part of all operating windows. It is the rate of air movement around a window, door, or skylight in the presence of a specific pressure difference across it. The lower the number, the less air flows through the window when it is closed and locked. Air leakage also depends on the proper installation of a window, which is assumed in all ratings.
Save Money, and Use Less Energy
Installing ENERGY-STAR® qualified windows and doors lowers energy bills and saves you money. Replacing old windows with ENERGY-STAR® certified windows lowers household energy bills by an average of 12 percent nationwide. Lower energy consumption also reduces greenhouse gas emissions from power plants and homes. Can you feel your carbon footprint shrinking?
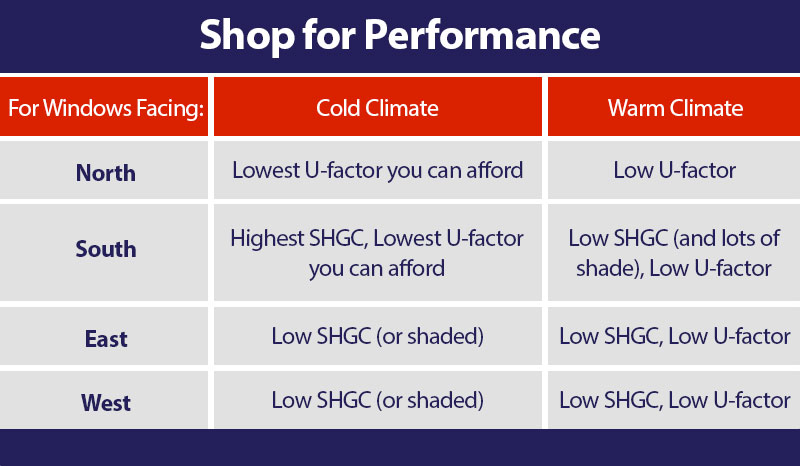
Shop for Windows that Perform Best for Your House
“Window orientation and window direction are important factors to enhance your savings and can increase the energy efficiency of your home, as well as make it more comfortable to live in. The orientation of the windows in your home can affect the lighting of the rooms resulting in electricity and heating consumption. For example, south-facing windows allow plenty of light into the room as the sun tracks mostly in the southern half of the sky. A north-facing window typically receives less natural light, so choosing the right size and high-performance glass can make a huge difference.
When shopping for windows, however, energy efficiency isn’t the only consideration. Here are a few other critical factors to keep in mind:
- Price: Establishing a budget is essential. Engaging with knowledgeable retailers can help you find windows that offer the best value for your money without compromising on quality.
- Materials: Windows come in various materials, each with distinct benefits. Consider options like vinyl for low maintenance, aluminum for durability, or wood for a classic look. Each material impacts the window’s performance and aesthetic.
- Sizes, Shapes, and Profiles: With countless styles and designs available, choosing the right fit is crucial. Accurate measurements ensure a seamless fit and optimal performance, preventing drafts and leaks.
By considering these additional factors alongside window orientation, you can make a well-rounded decision that enhances both the efficiency and appeal of your home.
Ask the Team at New Windows for America about how our windows can be specified with high-performance glass to meet ENERGY-STAR® criteria for our specific climate zone here in Colorado.
Exploring Window Materials: Making the Right Choice
When selecting the perfect windows for your home, the material you choose plays a crucial role. Here’s a breakdown of how different materials—vinyl, aluminum, fiberglass, and wood—impact both performance and aesthetics:
Vinyl Windows
Pros:
- Affordability: Vinyl windows are often the most budget-friendly option.
- Energy Efficiency: They’re excellent insulators, helping to reduce energy costs.
- Low Maintenance: These windows don’t require painting or refinishing, making them easy to care for.
Cons:
- Aesthetic Limitations: They may not offer as rich an appearance as wood.
- Color Choices: Over time, color options may fade under intense sunlight.
Aluminum Windows
Pros:
- Durability: Aluminum is resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for various climates.
- Strength: Its robust nature supports large glass panes, allowing for expansive views.
- Sleek Design: Provides a modern, minimalist look.
Cons:
- Poor Insulation: Aluminum conducts heat and cold, potentially impacting energy efficiency.
- Condensation Issues: May succumb to condensation, which can lead to moisture problems.
Fiberglass Windows
Pros:
- Strength and Stability: Fiberglass resists warping and expansions due to temperature changes.
- Energy Efficiency: Provides superior insulation, keeping your home comfortable.
- Variety of Finishes: Capable of mimicking the look of wood without the upkeep.
Cons:
- Cost: Generally more expensive than vinyl and aluminum.
- Limited Color Options: May not offer as broad a palette as other materials.
Wood Windows
Pros:
- Timeless Appeal: Offers a classic, elegant look that enhances home value.
- Customizable: Easy to paint or stain to match interior and exterior designs.
- Insulation: Natural insulating properties help maintain indoor temperatures.
Cons:
- Maintenance Required: Needs regular painting or staining to prevent rot and weather damage.
- Price: Tends to be more expensive than other materials, both initially and in maintenance.
Choosing the right window material depends on your specific needs and preferences. Whether you prioritize cost, aesthetics, or energy efficiency, understanding the characteristics of each material can guide you to the ideal decision for your home.
Ready to Replace Your Windows?
Ensure your windows are as energy efficient as possible to help you save energy, reduce your heating and cooling costs, and overall improvement of your comfort in your home. New Windows for America offers all kinds of different windows and doors, including ENERGY-STAR® rated windows and doors! New Windows for America has 25+ years of experience with installing windows, doors, and siding for your entire home! We are happy to work with you on finding the best window replacement for your Colorado home and can offer you a free estimate.
Contact our New Windows for America Team today and get a free estimate.